AVL树:古老的自平衡二叉搜索树
之前的 文章 介绍了什么是二叉搜索树,以及它的各项操作。但在代码实现的时候,只是给出了最简单的算法,并没有维持二叉搜索树的平衡。在极端情况下,二叉搜索树会退化为链表结构,从而导致搜索效率大幅下降,这是我们很不希望看到的。AVL 树就是一种自平衡二叉搜索树,也是最早的自平衡二叉搜索树,后面的很多平衡二叉树都是基于它来改进的,比如我们所熟知的红黑树,以及 splay 树等等。
AVL 树的基本定义
AVL 树的定义,其实是平衡性的定义。平衡这个概念,存在多种定义,AVL 树的平衡定义非常直接,每个节点的左右子树的高相差必须小于或等于 1。这个定义是比较严格的定义了,到 splay 树,平衡的定义又变了。
有人会对这个定义产生误解,认为整颗树上任意两个叶子节点的深度1差也必须小于或等于 1。这个要求过于严厉了些,如果按照这个说法,二叉树得是一个完全二叉树或是满二叉树,这在实际的应用中难以达到。AVL 树的要求仅仅是每个节点的左右两颗子树的高相差 1 或等高即可,这一定要注意。
AVL 树的平衡性实现
之前的二叉搜索树的 文章 提到,树的结构的改变仅仅会发生在插入或删除操作,因为这些操作会增加或移除树上的某个节点,使某个或某些节点的左右子树的高的差从原来的 1 变为 2,从而打破了平衡,此时就需要对树进行调整来恢复平衡。
如何调整?思路又是什么?整体思路其实就是定位到不平衡的地方,然后将这个地方变为平衡。找的话很好找,只需要在做插入或删除操作时进行同步勘查即可(每个节点信息中记录了该节点高),在插入的地方向上顺着路径去找,第一个不满足平衡性的节点就是需要调整的地方。难点在于如何将其变为平衡。
因为是二叉树,无非是那么几种情况,这里还是对所有的情况进行列举。
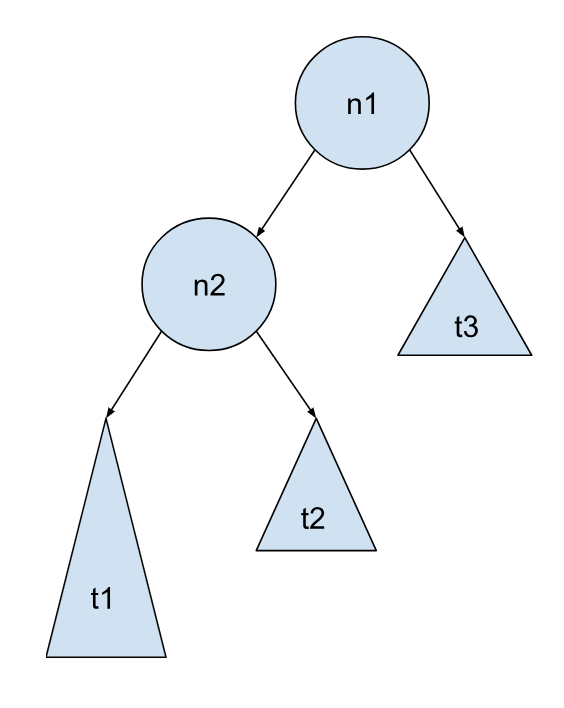
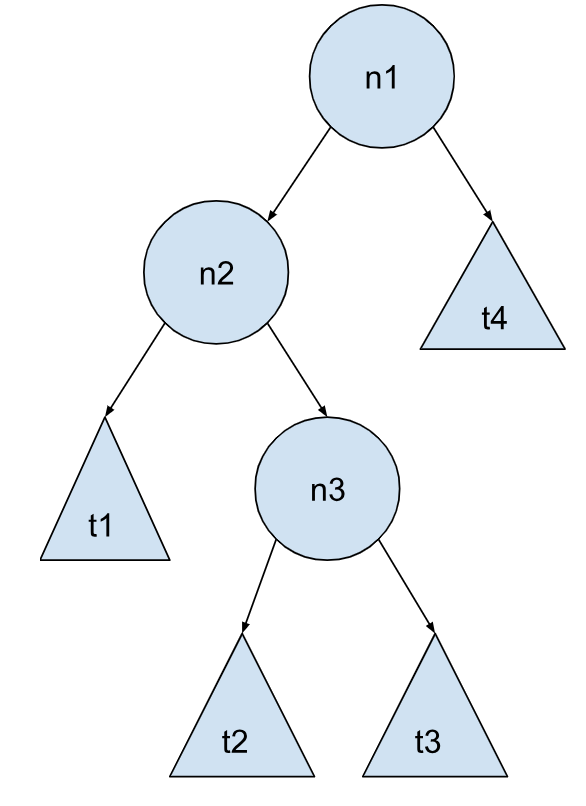
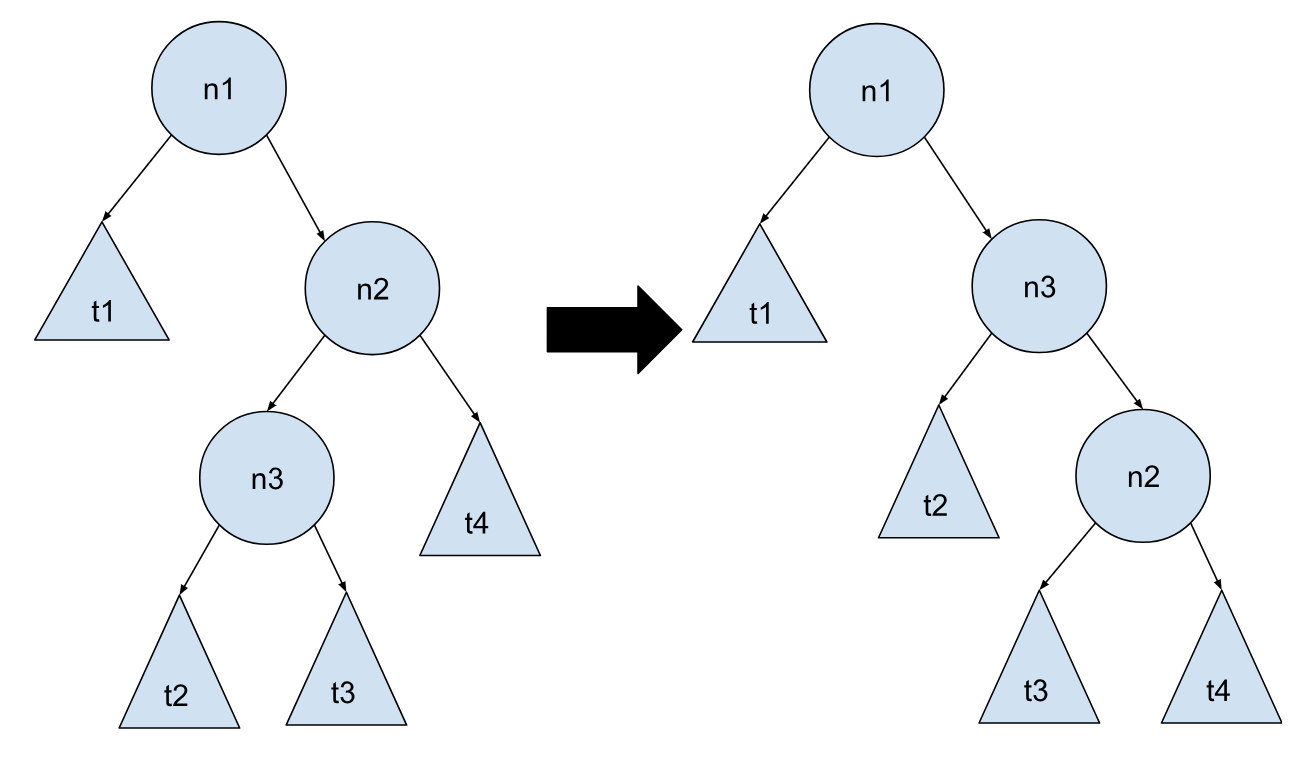
情况 1 - 插入发生在最左边的子树:
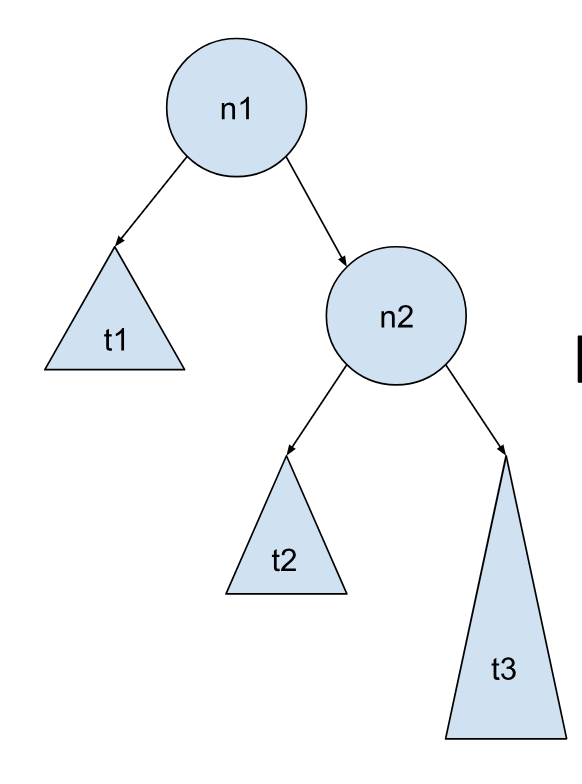
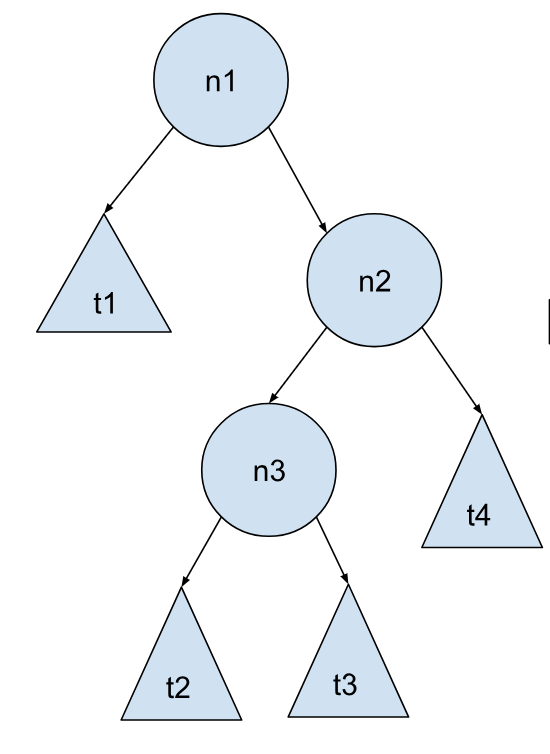
情况 2 - 插入发生在最右边的子树:
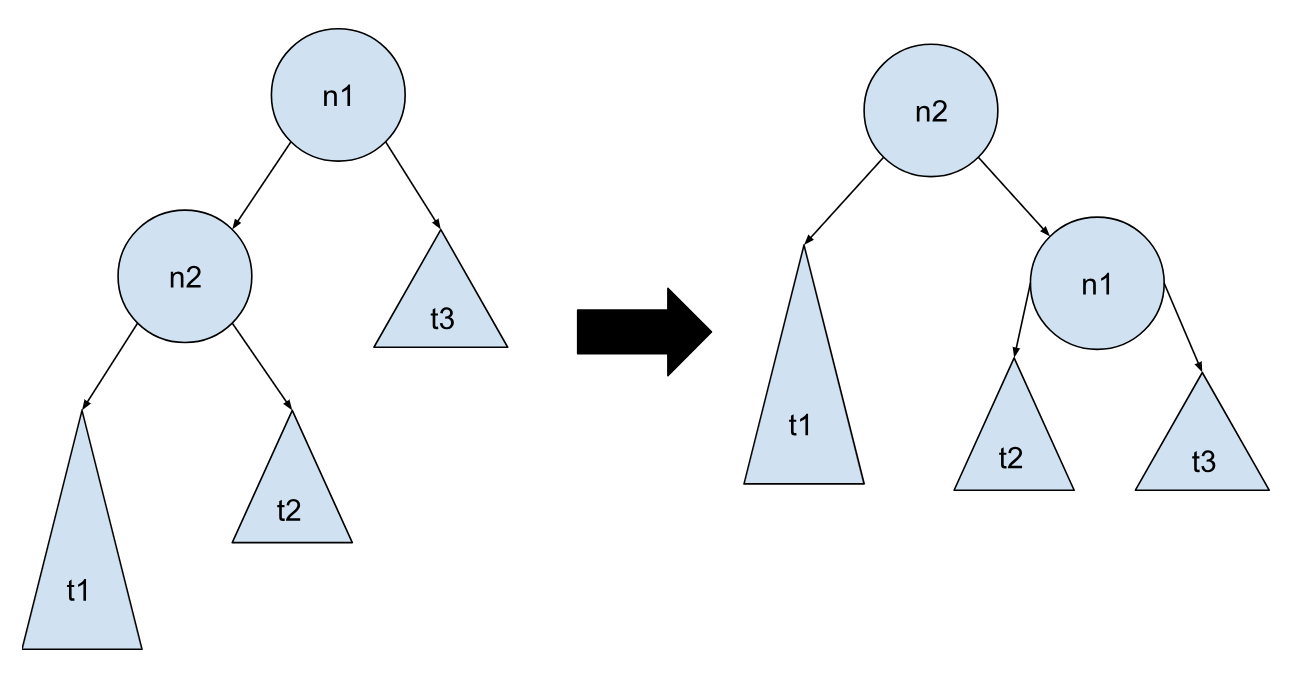
我们先来看看上面这两种情况,不平衡发生在 n1 节点处。拿情况 1 来说,这个高度差是由 t1 子树和 t3 子树造成的,需要尽量把 t1 子树上移,t3 子树下移。那具体怎么移呢?试着试着,就会发现,将 n1 节点和 n2 节点互换位置,答案便有了。在它们互换位置的同时,它们的子树也要根据二叉搜索树的定义进行相应的调整,对于情况 1 就如下图所展示的这样进行相应的变换就可以得到我们想要的结果:
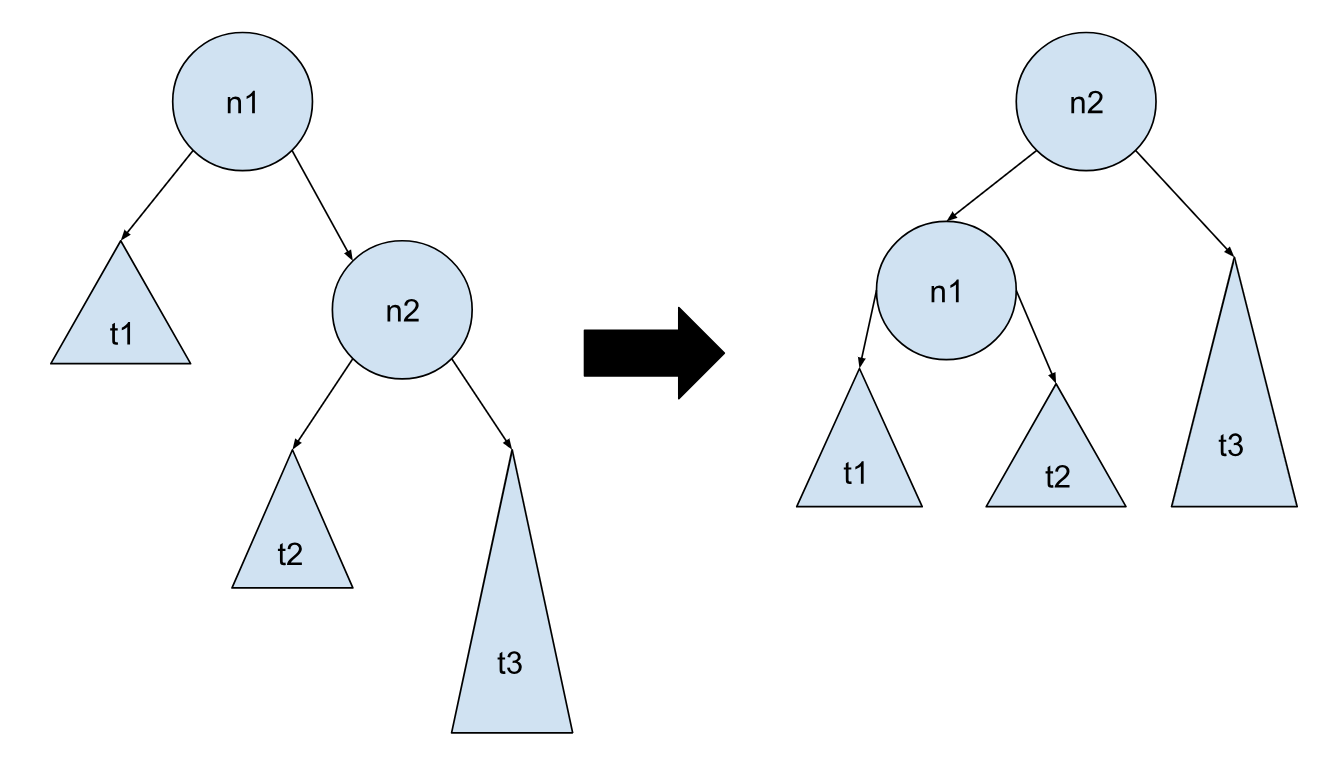
情况 2 其实是情况 1 的对称情况,操作和情况 1 类似,把左右颠倒即可:
剩下还有两种情况,相比于上面的两种情况,会复杂些
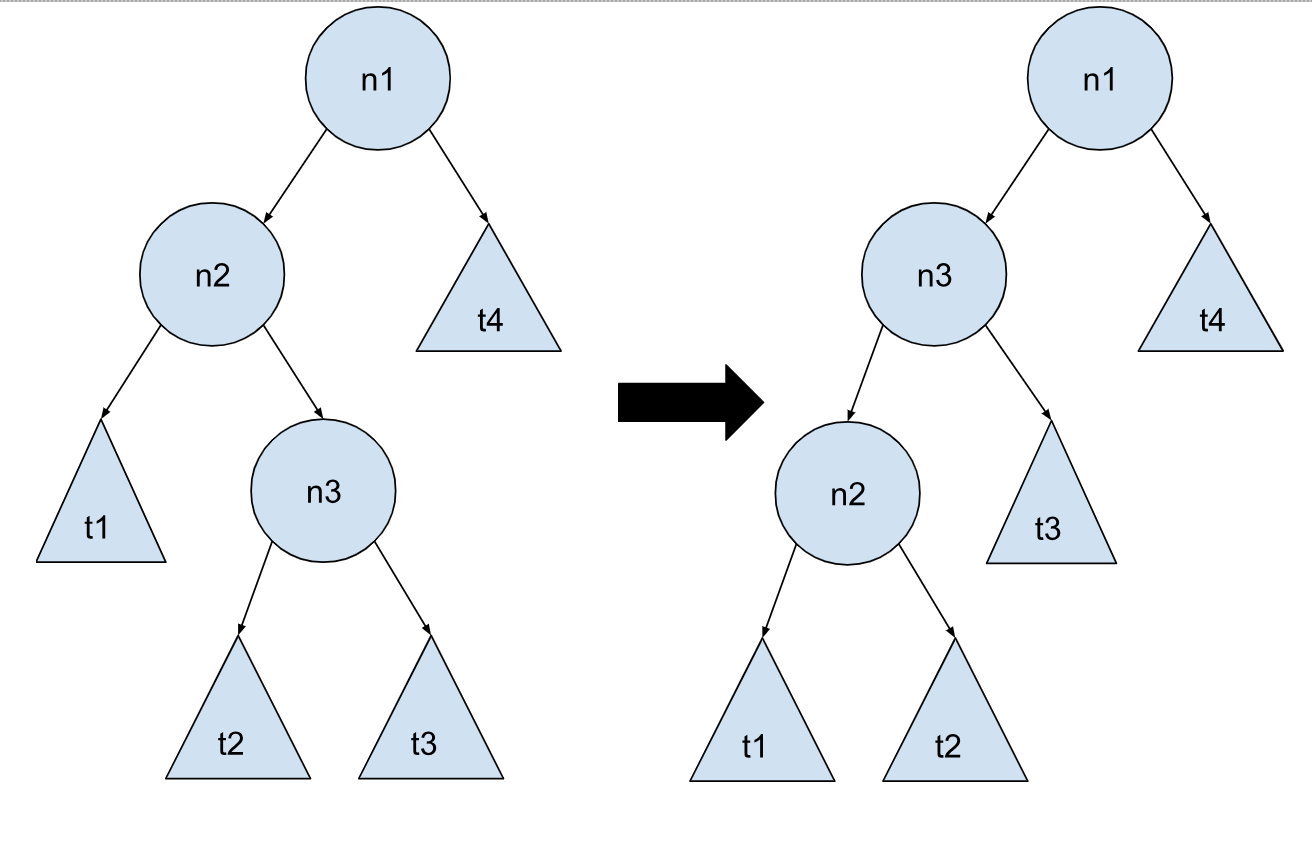
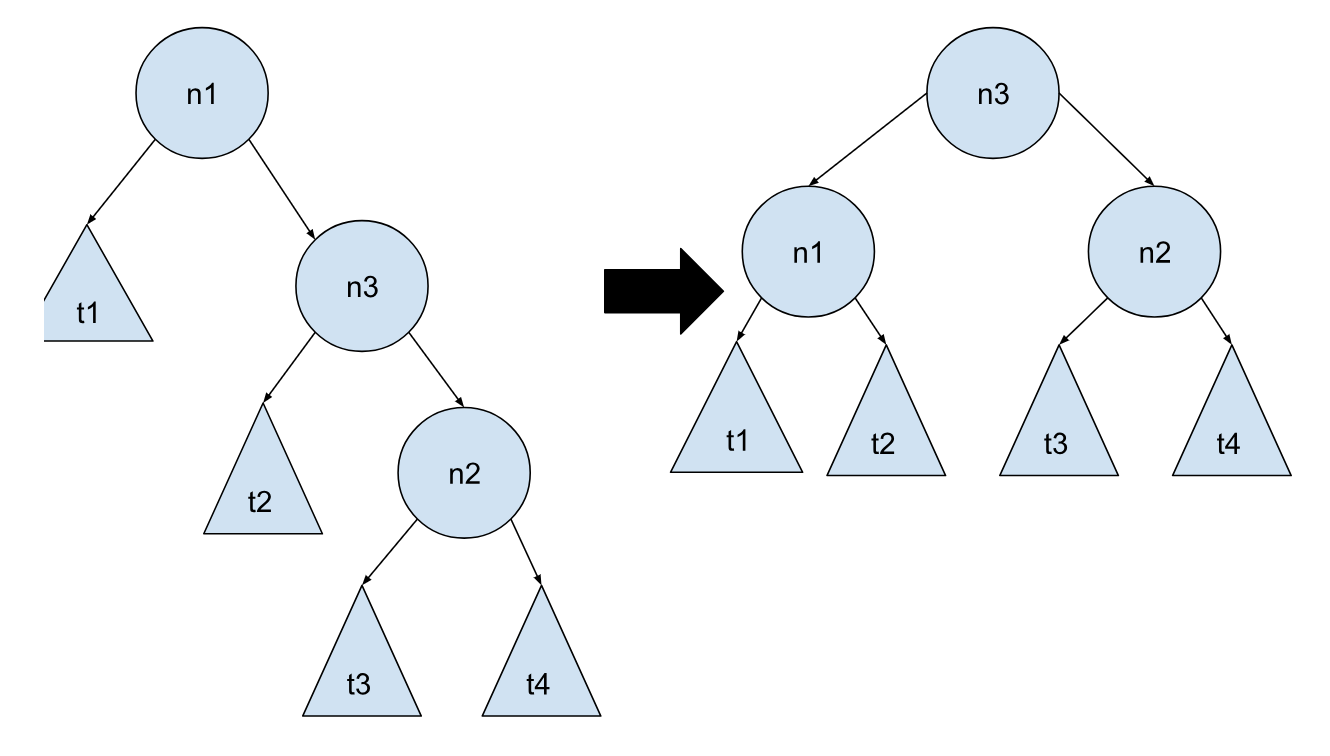
情况 3:
情况 4:
这两种情况和之前的一样,也是对称的,一种情况可以根据另一种情况如法炮制。之前的两种情况插入的点在最左边或最右边的子树,但是当插入的点在中间的时候,套用之前的方法就行不通了。为了方便展示节点的移动,这里把中间的子树画成是一个节点带两颗子树,这两颗子树我画的是一样高,但是他们按道理来说可以不一样高的,也可以是空的,但这都不是重点,重点是不平衡发生了,就拿情况 3 来举例,要尽量把 n3 所代表的子树往上移,把 t4 子树往下移。之所以会比前两个情况复杂,是因为现在有 3 个节点要考虑,但思路还是交换节点,这里我们想要尽量把 n3 往上移,最好是移到 n1 的位置。之前的例子中的交换是在父子之间进行的,那么这里有没有一种可能,我们进行两次交换,子节点先和父节点交换,然后再和祖父节点进行交换。尝试下来,最后的结果就是我们想要的:
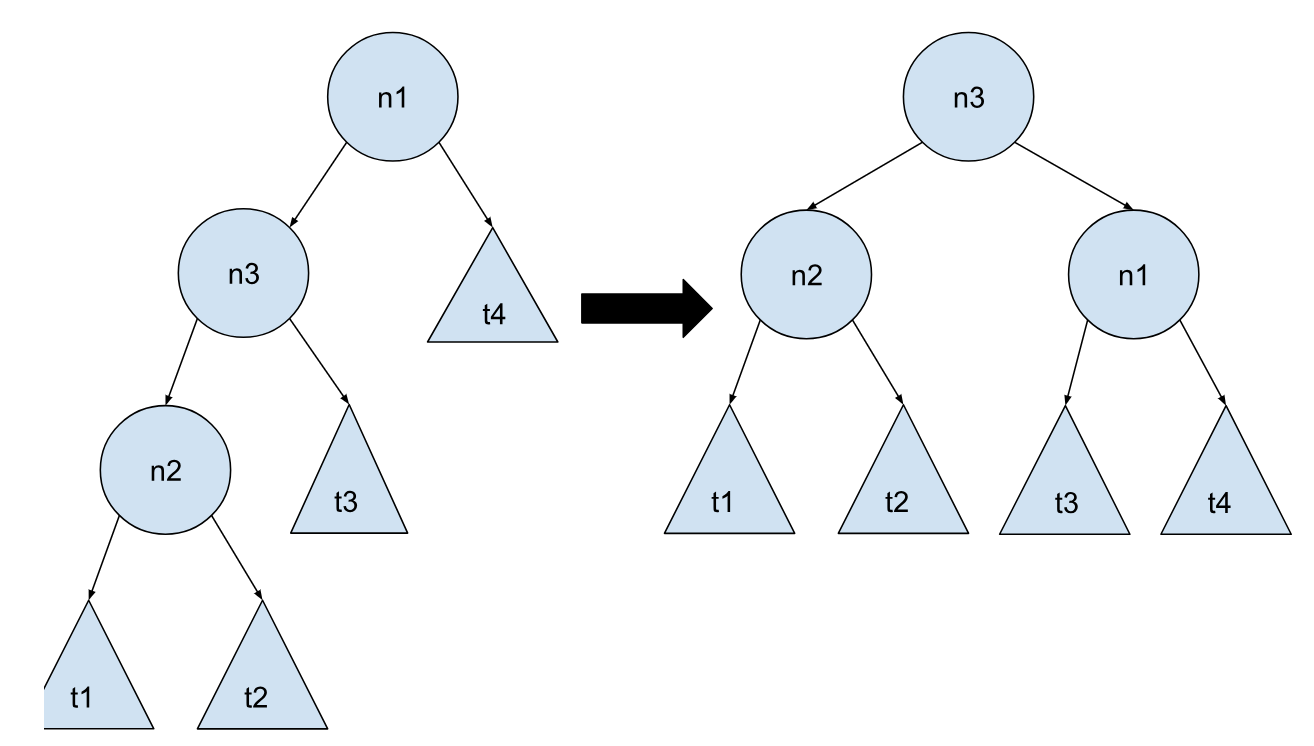
对于情况 3 来说,我们先进行一次交换,使 n3 和 n2 的位置发生交换,这一步做完,你再想想,这个是不是就是情况 1?
接着我们再让 n3 和 n1 进行位置交换
之前的 t2 t3 子树向上挪了一格,它们和 t4 子树的高度差也缩小了,我们的目的达到了。
情况 4 是和情况 3 一样的,无非是左右互换:
代码实现
我们先来看看有关平衡性调整的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
private int height(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
return t == null ? -1 : t.height;
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> balance(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
if (t == null) {
return t;
}
if (height(t.left) - height(t.right) > 1) {
if (height(t.left.left) >= height(t.left.right)) {
// 情况 1
t = rotateWithLeftChild(t);
} else {
// 情况 3
t = doubleWithLeftChild(t);
}
} else if (height(t.right) - height(t.left) > 1) {
if (height(t.right.right) >= height(t.right.left)) {
// 情况 2
t = rotateWithRightChild(t);
} else {
// 情况 4
t = doubleWithRightChild(t);
}
}
t.height = Math.max(height(t.left), height(t.right)) + 1;
return t;
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> rotateWithLeftChild(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
TreeNode<AnyType> tl = t.left;
t.left = tl.right;
tl.right = t;
t.height = Math.max(height(t.left), height(t.right)) + 1;
tl.height = Math.max(height(t.left), t.height) + 1;
return tl;
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> doubleWithLeftChild(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
t.left = rotateWithRightChild(t.left);
return rotateWithLeftChild(t);
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> rotateWithRightChild(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
TreeNode<AnyType> tr = t.right;
t.right = tr.left;
tr.left = t;
t.height = Math.max(height(t.right), height(t.left)) + 1;
tr.height = Math.max(height(t.right), t.height) + 1;
return tr;
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> doubleWithRightChild(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
t.right = rotateWithLeftChild(t.right);
return rotateWithRightChild(t);
}
只需要对照之前的图进行条件判断,然后相对应地交换子树位置即可,这里就不过多赘述。现在的问题是,光有平衡性的调整还不够啊,还必须和二叉搜索树的插入和删除操作结合起来,毕竟还需要借助插入和删除来找到需要进行平衡性调整的子树。我们可以把之前二叉搜索树的插入和删除的代码照搬过来,然后我们在这两个操作的最后加上平衡性调整即可,完整代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
public class AVLTree<AnyType extends Comparable<? super AnyType>> {
private static class TreeNode<AnyType> {
TreeNode<AnyType> left;
TreeNode<AnyType> right;
int height;
AnyType val;
TreeNode(AnyType val) {
this(val, null, null);
}
TreeNode(AnyType val, TreeNode<AnyType> left, TreeNode<AnyType> right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.height = 0;
}
}
private int height(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
return t == null ? -1 : t.height;
}
private static final int ALLOWED_IMBALANCE = 1;
private TreeNode<AnyType> insert(AnyType x, TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
if (t == null) {
return new TreeNode<>(x, null, null);
}
int compareResult = x.compareTo(t.val);
if (compareResult < 0) {
t.left = insert(x, t.left);
} else if (compareResult > 0) {
t.right = insert(x, t.right);
}
return balance(t);
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> remove(AnyType x, TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
if (t == null) {
return t;
}
int compareResult = x.compareTo(t.val);
if (compareResult < 0) {
t.left = remove(x, t.left);
} else if (compareResult > 0) {
t.right = remove(x, t.right);
} else if (t.left != null && t.right != null) {
t.val = findMin(t.right).val;
t.right = remove(t.val, t.right);
} else {
t = (t.left != null) ? t.left : t.right;
}
return balance(t);
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> balance(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
if (t == null) {
return t;
}
if (height(t.left) - height(t.right) > ALLOWED_IMBALANCE) {
if (height(t.left.left) >= height(t.left.right)) {
// 情况 1
t = rotateWithLeftChild(t);
} else {
// 情况 3
t = doubleWithLeftChild(t);
}
} else if (height(t.right) - height(t.left) > ALLOWED_IMBALANCE) {
if (height(t.right.right) >= height(t.right.left)) {
// 情况 2
t = rotateWithRightChild(t);
} else {
// 情况 4
t = doubleWithRightChild(t);
}
}
t.height = Math.max(height(t.left), height(t.right)) + 1;
return t;
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> rotateWithLeftChild(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
TreeNode<AnyType> tl = t.left;
t.left = tl.right;
tl.right = t;
t.height = Math.max(height(t.left), height(t.right)) + 1;
tl.height = Math.max(height(t.left), t.height) + 1;
return tl;
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> doubleWithLeftChild(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
t.left = rotateWithRightChild(t.left);
return rotateWithLeftChild(t);
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> rotateWithRightChild(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
TreeNode<AnyType> tr = t.right;
t.right = tr.left;
tr.left = t;
t.height = Math.max(height(t.right), height(t.left)) + 1;
tr.height = Math.max(height(t.right), t.height) + 1;
return tr;
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> doubleWithRightChild(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
t.right = rotateWithLeftChild(t.right);
return rotateWithRightChild(t);
}
private TreeNode<AnyType> findMin(TreeNode<AnyType> t) {
if (t == null) {
return null;
} else if (t.left == null) {
return t;
}
return findMin(t.left);
}
// 测试用,可忽略
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVLTree<Integer> avl = new AVLTree();
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(2, null, null);
root.left = new TreeNode(1, null, null);
root.right = new TreeNode(3, null, null);
root = avl.insert(4, root);
root = avl.insert(5, root);
root = avl.insert(6, root);
root = avl.insert(7, root);
root = avl.insert(15, root);
root = avl.insert(16, root);
root = avl.insert(14, root);
root = avl.insert(13, root);
root = avl.insert(12, root);
root = avl.insert(11, root);
root = avl.insert(10, root);
root = avl.insert(9, root);
root = avl.insert(8, root);
System.out.println(root.val);
System.out.println(root.left.val);
System.out.println(root.right.val);
}
}